In our fast-paced digital world, the importance of cybersecurity is more crucial than ever. As businesses lean more on digital platforms, the cybersecurity industry is set to experience significant growth, with projections indicating it could reach a staggering US$298.5 billion by 2028, expanding at an impressive annual rate of 9.4%. This surge is largely driven by the pressing need for strong security measures, especially as the costs related to cyber crime (attacks and other types of digitally-based crime) are anticipated to hit an astonishing US$10.5 trillion each year by 2025.
IMF Warns That Global Financial Stability is Jeopardised By Cyber Threats
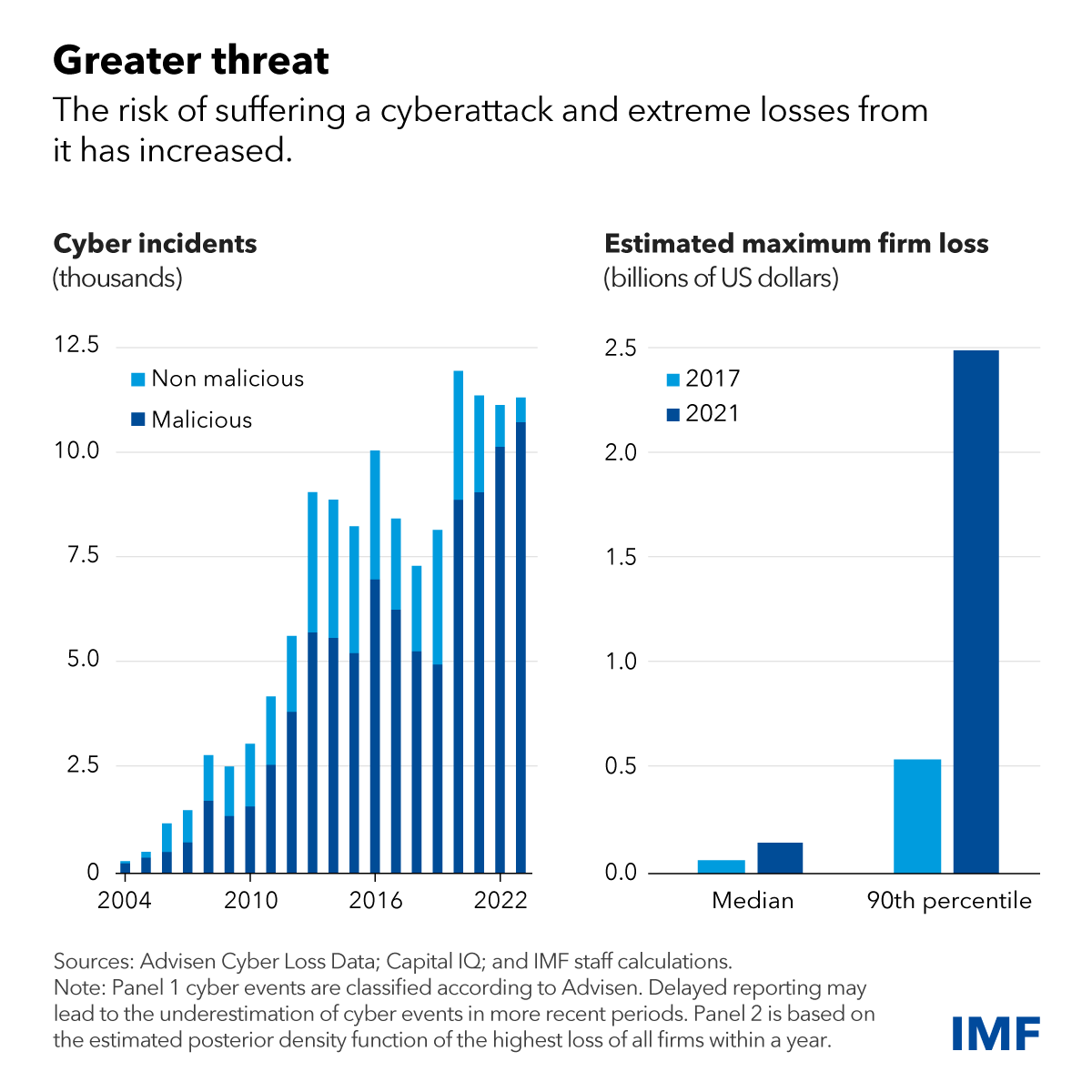
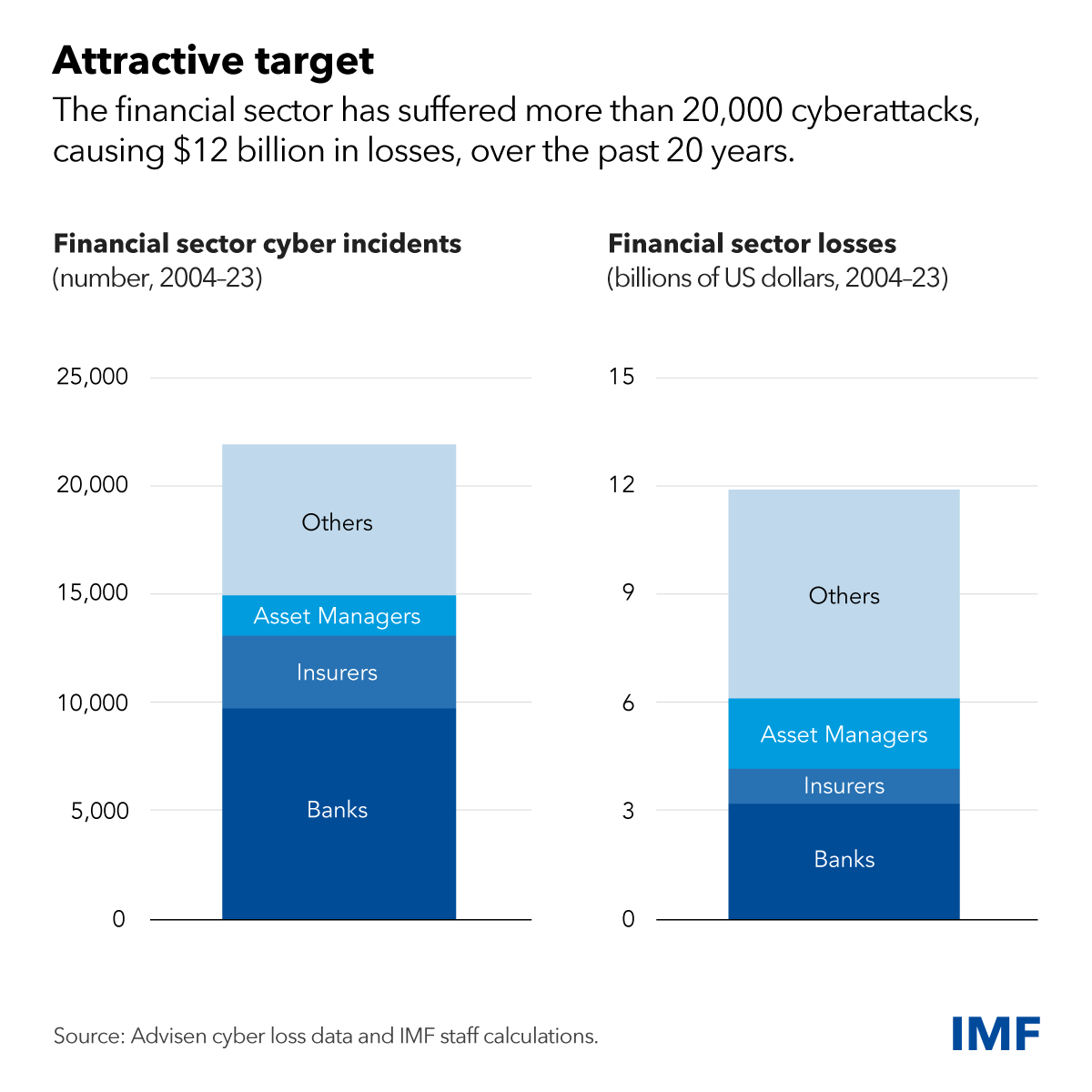
In the past two decades, nearly one-fifth of reported cyber incidents have affected the global financial sector, causing $12 billion in direct losses to financial firms, according to the IMF’s Global Financial Stability Report. Since 2020, direct losses amounted to an estimated $2.5 billion.
On one hand, the surge in cyber threats highlights just how crucial it is for organisations to bolster their cybersecurity measures. As these challenges grow more sophisticated, businesses are recognizing the importance of investing more heavily in robust cybersecurity solutions to protect their assets and sensitive information. This situation has created a sort of arms race where both cybercriminals and defenders are constantly adapting to outsmart one another.
With the rapid advancements in AI technology, this dynamic is only expected to intensify. Cyber attackers are increasingly leveraging AI to develop more effective strategies for their malicious activities, while organisations are also harnessing the power of AI to enhance their defences.
As organisations continue to shift to cloud environments, the demand for cloud security solutions has skyrocketed, with access control and privilege management becoming top priorities.
The adoption of zero-trust architecture is also on the rise, bringing notable benefits such as a better user experience and a simplified network structure. However, moving to this model can be a complex and costly endeavour, requiring careful planning and attention to existing systems.
Despite these challenges, investing in cybersecurity offers not just protection but also a valuable opportunity for businesses to enhance their security and operational efficiency. As we move through this intricate landscape, it’s evident that investing in cybersecurity will pay off for businesses, as the demand for advanced defence solutions is only going to grow in the future. Investors (as in, financial market participants) will also benefit, first through avoiding financial fallout from cyberattacks and second by investing in growing companies that provide these services.
What Should You Know About The Zero Trust Model?
The Zero Trust model is a cybersecurity framework that operates on the principle of “never trust, always verify.” It assumes that threats could be both external and internal, and therefore, no user or device should be trusted by default, regardless of their location within the network. This model emphasises strict identity verification, continuous monitoring, and least-privilege access to minimise the risk of data breaches and unauthorised access. By implementing Zero Trust, organisations aim to enhance their security posture in an increasingly complex threat landscape.
The Rise of a New Era: Generative AI in Cybersecurity
One of the most exciting developments in this space is the emergence of AI-driven threat detection systems, which greatly improve our ability to spot and respond to potential threats in real time, making information security processes more efficient and automated.
Generative AI is transforming cybersecurity by helping organisations strengthen their defences against evolving threats and making cybersecurity more proactive and resilient against sophisticated attacks.
Large Language Models (LLMs) are making significant strides in cybersecurity by enhancing various processes. They sift through vast data to identify new risks, keeping companies ahead of cybercriminals.
GenAI can be used not just for real-time threat intelligence analysis, but also in many different areas. This includes detecting phishing attempts, automating incident responses, analysing malware, managing vulnerabilities, providing security awareness training, assisting with chatbots, and identifying unusual activities, among other things. Detecting phishing attempts can be done through GenAI by examining the content of emails closely. LLMs also streamline incident response, generating actionable playbooks based on past data. In vulnerability management, they help prioritise threats relevant to an organisation.
According to Precedence Research, the market size for generative AI in cybersecurity was exhibited at $460 million in 2023 in the US, and it is projected to be worth around $4.19 billion by 2034, poised to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 22.24% from 2024 to 2034.
Transforming Cyber Defence: The Emergence of AI-Driven Intrusion Detection
Cyber intrusion detection is all about keeping a close eye on network traffic and system activities to spot any unauthorised access or unusual behaviour that might signal a breach. There are different methods used in this process. For instance, signature-based detection looks for specific patterns of known malicious activity, while anomaly-based detection focuses on identifying behaviours that deviate from what’s considered normal.
Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) can be set up either on individual hosts or across the network, providing real-time alerts to security teams when something seems off. This proactive approach allows organisations to respond quickly to potential threats, minimising any damage.
Integrating AI with cyber intrusion detection systems significantly boosts an organisation’s capacity to detect, respond to, and recover from cyber threats, resulting in a stronger security posture and a lowered risk of data breaches.
Cyber threats are anticipated to increase in the near future, resulting in a heightened demand for intrusion detection systems and threat detection response platforms.
Emerging Risks in The Next Generation of AI
The rapid advancement of AI technology brings significant cybersecurity risks that organisations need to address. Key threats include adversarial attacks, where manipulated inputs confuse AI models, and data poisoning, which compromises training data integrity. Other concerns involve model stealing, where attackers recreate proprietary models, and privacy invasions due to exposed personal data. AI can also automate phishing efforts and adapt malware, making it harder to detect. Additionally, AI is used for creating deep fakes and executing social engineering on a large scale, a major attack vector even prior to AI-based threats.
To mitigate these risks, organisations should develop strong security frameworks, conduct regular assessments, and train their staff while utilising AI for improved detection and resilience. Proactive strategies are crucial for defending against these evolving threats, creating opportunities for both new and established cybersecurity firms.
From an investor’s perspective, you might discover intriguing companies that are poised for significant growth and present excellent investment opportunities.
Platforms like Vectra AI’s Threat Detection and Response are leading the way by offering real-time monitoring and swift action against cyber intrusions. Vectra AI is part of growing Extended Detection and Response (XDR) market valued at $2.2 billion in 2023 and is expected to grow to $31.3 billion by 2032, according to Market Research Future.
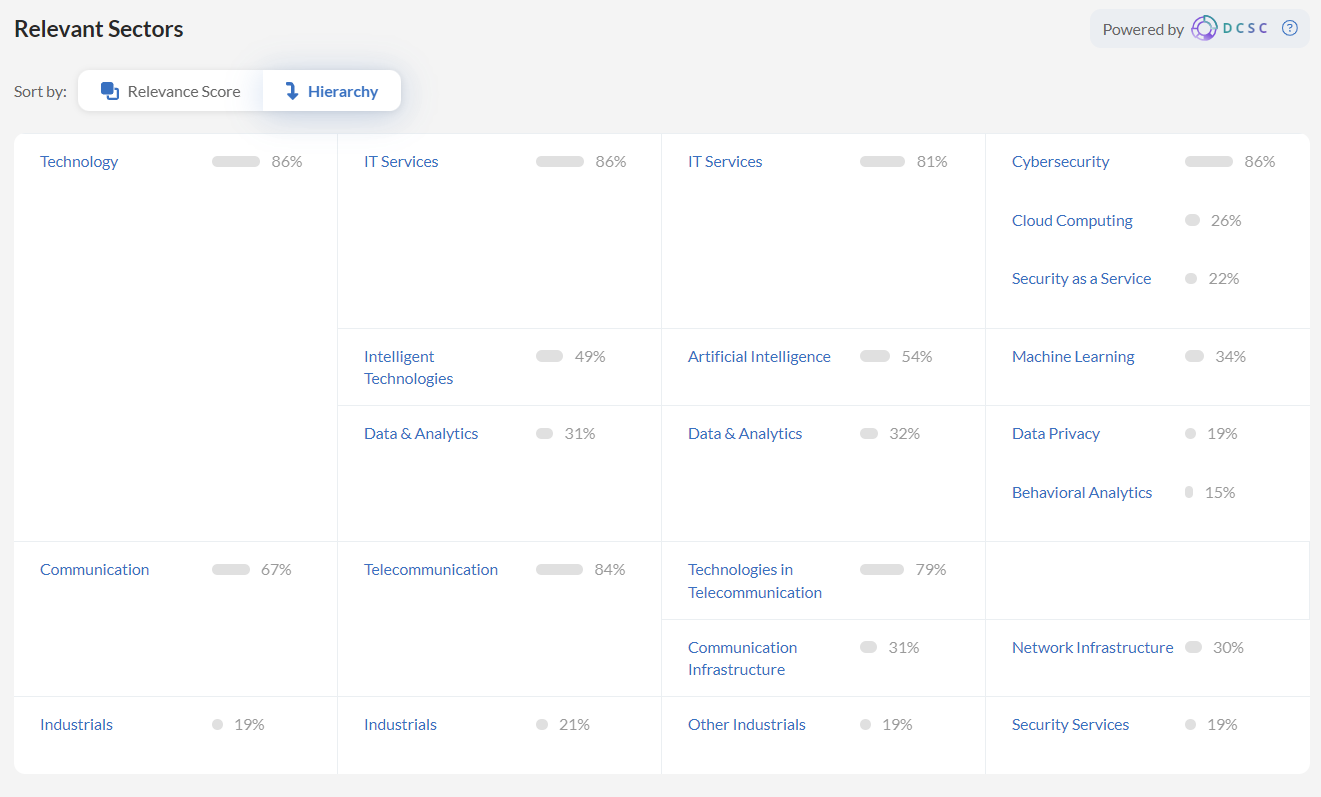
In this market segment, another prominent example is Darktrace, a rapidly expanding British cybersecurity company that leverages its AI to analyse data regardless of its location. It detects threats across the entire organisation, ensuring proactive cyber resilience.
Exactly what sector is Darktrace involved in, and what are similar companies? Investors can easily find out by using DCSC’s sector classification. Hint – it’s more than just one sector:
Then the most enticing sectors can be explored further for other constituent companies and their breakdowns.
OAuth and APIs: Simplifying Complex Concepts
OAuth is an authorisation framework enabling secure access to user data without sharing passwords. APIs serve as bridges for applications to communicate, facilitating seamless data exchange. However, misconfigurations in OAuth can lead to unauthorised access and data breaches. Similarly, weaknesses in APIs can expose sensitive information, making robust security measures essential.
The shift towards AI in threat detection and response marks a significant change in cybersecurity, promising not only improved security but also greater operational efficiency. However, like any technology, it’s crucial to continue researching and adapting to fully leverage its potential while tackling its inherent challenges. Ultimately, integrating AI into threat detection represents a major advancement, equipping businesses with the necessary tools to navigate the ever-evolving landscape of cyber threats.
Cloud Security and Zero-Trust Architecture Markets
As organisations increasingly turn to cloud-based security solutions, adopting zero-trust architecture has become a crucial strategy for protecting sensitive data. The global cloud security market size was valued at $35.8 billion in 2022 and is projected to reach $125.8 billion by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 13.6% from 2023 to 2032. This move towards cloud security not only boosts scalability but also significantly reduces the risks associated with data breaches.
Adopting a zero-trust model allows businesses to thoroughly verify every access request, regardless of the user’s location, thereby enhancing their overall cybersecurity posture.
Transitioning to a zero-trust framework does come with its challenges. Initial costs can be high, legacy applications may need updating, and there’s the potential for security gaps that can complicate the implementation process. Nevertheless, the long-term advantages — such as improved operational efficiency and enhanced protection against emerging threats — justify the investment for organisations.
In 2023, the market for zero trust architecture was valued at $18 billion. It is projected to expand to $41 billion by the end of 2036, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 18% throughout the forecast period from 2024 to 2036. This surge is largely fuelled by the growing threat of cyberattacks, the shift toward remote work, and the increasing need for compliance with regulations.
The security of remote work is increasingly becoming a top priority as well, effecting the cloud security market. The global market for remote work security is driven by a broader adoption of cloud security practices to protect data and applications. According to Allied Market Research, the remote work security market is projected to soar to $322.6 billion by 2032, with an impressive CAGR of 22.1%.
Numerous organisations are adopting zero trust models to enhance the security of their cloud environments and support their digital transformation initiatives in remote work situations. As businesses place a higher priority on security, the zero-trust approach is becoming an essential part of their modern cybersecurity strategies, helping them navigate the complex landscape of today’s digital world.
This development opens up exciting new opportunities for investors in the rapidly evolving fields of cloud security, remote work security and data protection applications. Additionally, there is significant potential for growth in companies that specialise in zero-trust security models. By investing in these areas, stakeholders can position themselves at the forefront of the security landscape. As the demand for robust security solutions continues to rise, these sectors are likely to offer promising returns.
The Dark Side of GPT: A New Frontier of Intrusion Detection
WormGPT and DarkGPT are cutting-edge AI models that have made their mark in the world of cybersecurity, especially in the area of cyber intrusion detection systems (IDS). These tools can generate highly convincing text, allowing cybercriminals to craft realistic phishing emails, develop malware, or even automate their attacks, creating serious risks for organisations.
The impact of these AI-driven technologies is significant. They empower attackers, making it easier for them to slip past traditional security defences and leading to a surge in both the number and complexity of cyber threats. In response, organisations need to evolve their intrusion detection systems to effectively spot and counter these AI-generated attacks. This means incorporating advanced machine learning algorithms that can analyse behaviour patterns and identify unusual activities that signal potential intrusions. The emergence of these technologies highlights the pressing need for organisations to continually monitor and update their cybersecurity posture to protect against increasingly sophisticated threats. This is contributing to a persistent growth in demand for different sectors of cybersecurity.
Cybersecurity Opportunities in Other Industries
The cybersecurity sector is experiencing remarkable growth and is opening up exciting opportunities across various industries, including finance, critical infrastructure, and healthcare.
In the financial world, institutions are stepping up their game by incorporating cutting-edge cybersecurity measures to protect their operations and customer information. For instance, numerous banks are adopting AI-powered threat detection systems and implementing the zero-trust architectures previously discussed, greatly enhancing their capacity to identify and respond to cyber threats in real time and proactively. This forward-thinking stance is crucial, especially since financial institutions are prime targets for cyberattacks that can lead to severe financial consequences.
In healthcare, the emphasis on cybersecurity is just as vital, especially with the increasing prevalence of the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT). Initiatives like CYMEDSEC are leading the charge to secure medical devices, ensuring that patient data remains safe while also enhancing operational efficiency. The importance of cybersecurity in healthcare cannot be overstated, as breaches can have direct implications for patient safety and trust.
What is the Internet of Medical Things and CYMEDSEC?
The Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) refers to a network of connected medical devices and applications that collect, transmit, and analyse health data. This ecosystem includes wearable devices, remote monitoring tools, and smart medical equipment, all designed to improve patient care, enhance operational efficiency, and enable real-time health monitoring. In a short summary, by leveraging IoMT, healthcare providers can gain insights into patient health, facilitate timely interventions, and promote personalised treatment strategies.
CyMedSec, or Cybersecurity in Medical Devices and Health Systems, is a community dedicated to addressing cybersecurity challenges in healthcare, particularly regarding medical devices. It promotes best practices and knowledge sharing to protect sensitive health information. The initiative fosters collaboration among healthcare, cybersecurity, and regulatory professionals to enhance the resilience of health systems against cyber threats.
When it comes to critical infrastructure, efforts spearheaded by the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) are harnessing advanced data analytics and cybersecurity technologies to strengthen security protocols. More and more companies are turning to cloud security solutions from providers like AWS and Google Cloud, which offer powerful protections, including enhanced cryptographic isolation and data protection during use. These innovations not only bolster security but also help streamline operations, allowing organisations to concentrate on their primary missions while effectively managing risks.
As these industries increasingly adopt advancements in cybersecurity, the potential for growth and improved resilience against emerging threats becomes clearer. This positions them at the forefront of the cybersecurity landscape, ready to tackle the challenges of the digital age.
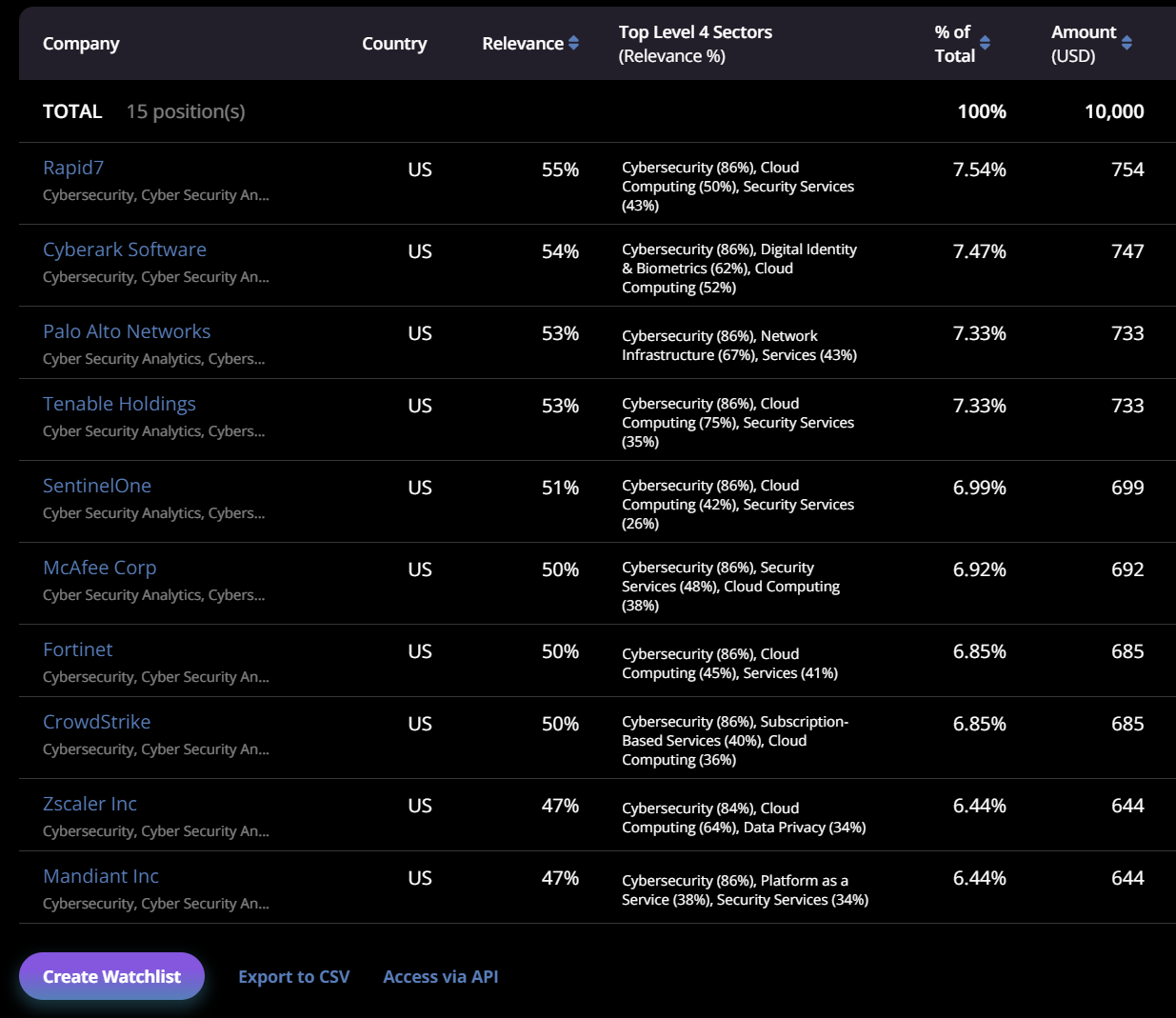
Leveraging DCSC.ai for Investment Opportunities
To successfully navigate the expanding world of cybersecurity investment opportunities, investors can turn to DCSC.ai, a cutting-edge AI-driven platform that classifies various sectors.
Our innovative tool provides real-time insights that are essential for discovering promising ventures in the cybersecurity realm. With its unique company-sector relevance scores, DCSC helps investors find organisations that could be involved with the anticipated growth in the cybersecurity market, which is projected to soar from around $193.73 billion in 2024 to $562.72 billion by 2032 — a CAGR of 14.3%.
What sets DCSC apart from traditional sector classification systems is its ability to deliver up-to-date data and insights, empowering investors to make informed choices using data right now, not as it was months or years ago. In a rapidly changing market, this means they can stay ahead of current trends and even anticipate future developments. With the market expected to grow rapidly, DCSC offers a valuable resource for early identification of key players.
Additionally, the platform’s flexible classification features allow for focused thematic research, enabling investors to craft intelligent portfolios that align with emerging trends in cybersecurity. By tapping into the capabilities of DCSC, investors can strategically position themselves to seize the vast opportunities available in the cybersecurity sector, ultimately enhancing their investment results in a landscape defined by rapid change and innovation.
The Future of Cybersecurity
As we gaze into the future of cybersecurity, we’re on the brink of exciting transformations that promise to redefine the landscape. One of the most significant shifts will be the enhanced role of artificial intelligence in threat detection. Thanks to evolving machine learning technologies, we can expect systems to become increasingly adept at anticipating and neutralising threats before they even arise. This forward-thinking approach will be essential as cyber adversaries refine their tactics, pushing us to move from merely reacting to threats towards anticipating them.
Quantum encryption is emerging as a revolutionary method for securing communications, making interception detectable and significantly enhancing information security. Automated incident response systems, such as SOAR platforms, allow organisations to react swiftly to security incidents, minimising damage and response times.
Rapid advancements in AI, quantum encryption, and automated incident response systems offer a distinctive opportunity for investors. For instance, quantum computing is set to be a game-changing technology that will unlock new market possibilities, paving the way for exciting investment opportunities and fundamentally reshaping future industries.
By making strategic investments in this dynamic field, you can take advantage of the increasing demand for cutting-edge cybersecurity solutions, enhancing your portfolio’s potential for significant returns while also contributing to a more secure digital landscape.
The Future of the (Digital) Battlefield
The United States National Intelligence Council’s report, “The Future of the Battlefield,” forecasts significant changes in military conflict over the next two decades, driven by emerging technologies and evolving doctrines. Key areas of focus include connectivity, lethality, autonomy, and sustainability, which will redefine warfare dynamics.
Case studies, such as the increasing use of AI and robotics by state and non-state actors, reveal how adversaries will leverage real-time information for tactical advantages. (The report highlights historical parallels, comparing future technological shifts to past military innovations, emphasising the complexity of predicting warfare’s evolution.)
On the digital battlefield, military units are increasingly deploying drone swarms that leverage AI for autonomous coordination during reconnaissance missions. Cyber warfare strategies are evolving, with nations targeting critical infrastructure to disrupt enemy operations and create chaos.
Augmented reality (AR) technology is enhancing situational awareness for soldiers, providing real-time overlays of maps and enemy positions to improve decision-making. Additionally, blockchain technology is being utilised for secure communications, ensuring tamper-proof messaging between military units.
The balance of power may hinge on information superiority as militaries strive for effective communication and data analysis capabilities. As cutting-edge technologies proliferate, the vulnerability of assets increases, potentially leading to higher escalation risks. In the near future, the emergence of transformative AI will profoundly alter the characteristics of battlefields.
Zero-trust architecture could become the norm, ensuring every access request undergoes rigorous verification. This strategy will play a crucial role in minimising the risk of data breaches. As more organisations transition to cloud-based environments, the demand for comprehensive cloud security solutions will grow, underscoring the need for adaptable security frameworks that can respond to emerging vulnerabilities.
On top of that, the cybersecurity market is expected to experience substantial growth, with investment in innovative technologies promising significant returns. Companies prioritising cybersecurity won’t just be protecting their assets; they’ll also boost their operational efficiency and gain a competitive edge in their industries. Given the rising financial stakes tied to cyberattacks, staying ahead of potential threats will be more important than ever.
All along the way, investors will be supporting new companies in the space, and finding them can be as easy as adding a couple related industries in DCSC’s Smart Portfolios tool.

Leave a Reply