The space technology sector is quickly becoming one of the most exciting and profitable industries out there. The global space economy will be worth $1.8 trillion by 2035, up from $630 billion in 2023 – almost twice the rate of global GDP growth according to World Economic Forum research, the potential for significant returns on investment is immense. This growth is largely driven by groundbreaking advancements in reusable rockets, satellite technology, and travel to low Earth orbit (LEO).
Innovations in Reusable Rockets
The rise of reusable rockets is transforming how we access and explore space, with leaders like SpaceX and Blue Origin at the forefront. For example, SpaceX has poured over $1 billion into reusable launch technologies, which has drastically cut costs and improved launch capabilities. Meanwhile, startups like Stoke Space, with backing from Bill Gates’ climate investment firm, are also making waves with their fully reusable systems, drawing in around $100 million in investments. These innovations have the potential to slash launch costs by as much as 70%, paving the way for more satellite launches and space exploration.
Reusables in Maintenance and Counterspace Activities?
It’s not just reusable rockets. China’s experimental reusable space plane made headlines as it returned to Earth after an impressive 267 days in orbit, completing its third mission. Launched on December 14, 2023, from Jiuquan spaceport, the mission showcased China’s advancements in reusable spacecraft technology, with Chinese state media emphasising its potential for more affordable and convenient space travel in the future. Notably, the spaceplane’s journey mirrored that of the U.S. X-37B, hinting at a competitive edge in orbital technology.
While the mission details remain largely under wraps, experts suggest the spacecraft engaged in rendezvous and proximity operations with a small satellite it released, which could have implications for satellite maintenance or even counter space activities. Despite the secrecy, the mission signifies China’s commitment to enhancing its space capabilities, supported by national funding for its development – and thus more government backing for the industry, which investors could eventually capitalise on.
As the spaceplane prepares for future missions, the timeline between landings will be crucial for assessing its reusability. This successful return underscores China’s growing maturity in space technology and its ambition to establish a more robust presence in the cosmos.
New Era in Space Travel
Radian Aerospace is on the brink of transforming space travel with its innovative spaceplane, Radian One, designed to replace traditional vertical rocket launches. This fully reusable vehicle aims to make space missions more efficient and accessible, utilising a unique rocket-powered sled system that allows it to launch horizontally like a jet. Founded in 2016, Radian Aerospace seeks to revive the dream of Single-Stage-To-Orbit (SSTO) technology, a vision that was once explored by NASA but ultimately shelved.
CEO Richard Humphrey envisions a future where space travel is as straightforward as a commercial flight, focusing on missions that enhance life on Earth, such as scientific research and satellite deployment, rather than tourism. The Radian One can potentially undertake up to 100 missions with rapid turnaround times, relaunching just 48 hours after landing.
With its capability to carry five crew members and remain in orbit for up to five days, the spaceplane represents a significant leap forward in space exploration. Radian Aerospace plans to have a full-size version ready by 2028, promising a new era in space travel that could open limitless opportunities for humanity.
“Imagine being able to detect wildfires in any country within minutes, identify oil and gas methane emissions in real time for remediation, or verify carbon stocks globally to enable large-scale carbon offset markets,” said Carmichael Roberts, co-leader of the Breakthrough Energy Ventures investment committee. “These are just a few of the far-reaching opportunities that greater access to space can provide through advanced satellite technology.”
Or, imagine a future where launching a satellite into orbit is as routine as booking a flight—this is becoming a reality thanks to these advancements. And investors who keep their eyes on the industry could see their capital take a similar trajectory to the reusable rockets (hopefully only on the way up though).
Satellite Technology and LEO Travel
The leap in satellite technology, especially with networks like Starlink and OneWeb, is revolutionising global logistics and telecommunications. These satellite constellations provide high-speed internet access around the globe, even in the most isolated areas, enhancing connectivity and enabling real-time data transfer.
The global market for LEO satellites was valued at USD 33.37 billion in 2023. The market is expected to grow at a 13.4% compound annual growth rate (CAGR) during the forecast period of 2024-2032. The LEO satellite market size is anticipated to grow to USD 102.90 billion by 2032.
This growth is further fuelled by the increasing need for precise asset tracking and monitoring capabilities, essential for modern supply chains and logistics operations.
Moreover, LEO travel is emerging as an exciting new frontier in space tourism, creating significant investment opportunities. The synergy between reusable rocket technology and advanced satellite systems is not only making space more accessible but is also laying the groundwork for a new era of exploration and tourism.
Global Navigation Satellite Systems
Everyone knows GPS, the US-based system built over the decades. However, more countries and regions are entering the industry, and Galileo and BeiDou are two prominent global navigation satellite systems (GNSS) that significantly enhance logistics and supply chain operations worldwide.
Galileo, the European Union’s GNSS, provides high-precision positioning services with an accuracy of up to one metre. Its advanced features, such as Search and Rescue (SAR) capabilities, enable rapid response times in emergencies, making it invaluable for logistics companies that prioritise safety and efficiency. With its strong integration into the European transportation infrastructure, Galileo enhances the reliability and accuracy of vehicle tracking, asset management, and route optimisation, ultimately leading to more efficient logistics operations across Europe and beyond.
The BeiDou Navigation Satellite System (BDS), developed by China, offers comprehensive global coverage and is particularly vital for logistics within Asia. With a focus on providing services tailored to the unique needs of the region, BeiDou supports real-time tracking and positioning, facilitating efficient fleet management and supply chain coordination. Its capabilities extend to precise timing and synchronisation, which are crucial for managing logistics operations, reducing delays, and improving overall service delivery.
Together, Galileo and BeiDou complement existing GNSS systems, enhancing global logistics capabilities through improved accuracy, reliability, and real-time data, which are essential for modern supply chain management. As more satellite constellations come online with more features, there is more opportunity for niche markets to spring up and bring new goods and services to the public.
The Growing Demand for Space Experience
The innovations we’re seeing in the space industry are opening doors to entirely new business models and investment opportunities today.
The emergence of reusable rockets and advanced satellite systems has significantly lowered the costs associated with space access, creating a fertile ground for diverse commercial opportunities.
The Space Travel or Tourism market industry is projected to grow from USD 110.7 billion in 2024 USD 3,743.4 Million by 2032, exhibiting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 55.3% during the forecast period (2024 – 2032).
These figures highlight the transformative potential of the space sector, increasingly driven by private investments and collaborations between public and private entities.
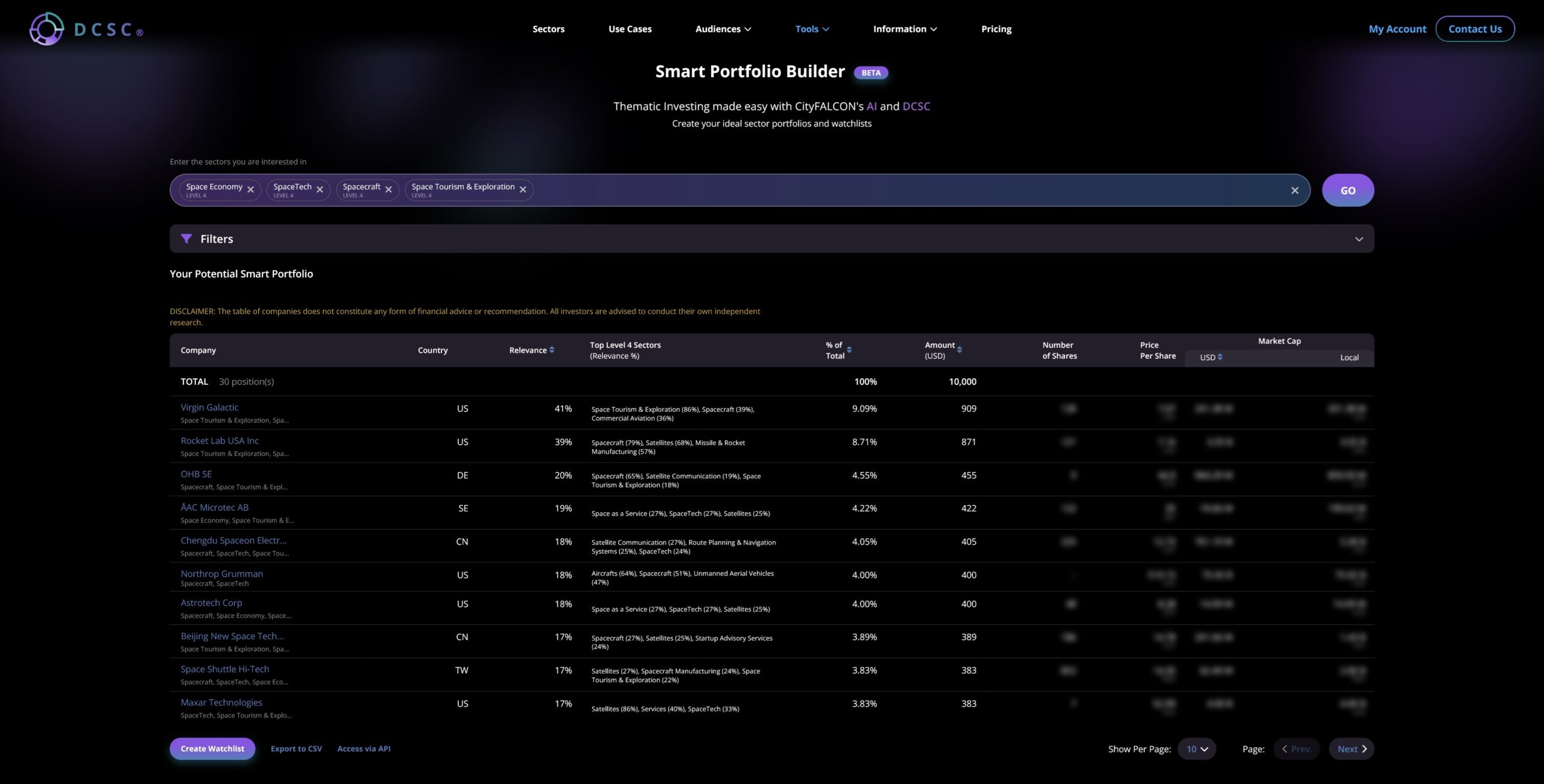
How do investors find these opportunities? One way is through sector-based thematic investing. DCSC.ai’s company-sector classification system allows you to navigate the evolving landscape of the space industry, offering investors a sophisticated, AI-driven tool to identify and seize emerging opportunities. Utilise our classification framework to discover prospects in the space sector and their degree of relevance, enabling you to pinpoint both budding startups and established companies for more informed investment choices.
Mining the Cosmos: The Future of Resource Extraction in Space
Asteroid mining represents a revolutionary step in humanity’s quest to harness the resources of the cosmos. Space mining, particularly asteroid mining, is an emerging field that holds significant promise for resource acquisition beyond Earth. Companies like Planetary Resources and Deep Space Industries are at the forefront, exploring the feasibility of extracting valuable metals such as gold, platinum, and rare earth elements from asteroids.
These celestial bodies are believed to contain vast amounts of resources that could be more accessible than terrestrial mining. The potential for asteroid mining could alleviate resource scarcity on Earth and reduce the environmental impact of traditional mining practices. It could even change the economics of the industries, wherein rare or precious resources become commonplace.
Furthermore, the technology developed for asteroid mining could pave the way for in-situ resource utilisation, allowing for the production of fuel, water, and building materials in space. This capability would support long-duration space missions, including those aimed at Mars and beyond.
The economic impact is expected to be significant ushering in a new age of space commerce. The asteroid mining market is projected to reach USD 8.40 billion by 2033, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 16.53% from 2023 to 2033, which is incredible seeing as we currently cannot mine asteroids at all.
For investors looking to navigate this complex and rapidly changing landscape, DCSC.ai again provides a valuable resource, this time with emerging trends, which could include the space mining sector as it does emerge (as yet a future prospect only).
For existing space companies, you can still see which sectors they’re related to. In an sector as high-tech as the space industry, there can be plenty of intersector involvement.
The Next Era in Space Technology
Starlink, developed by SpaceX, is revolutionising the space industry by providing global high-speed internet coverage through a constellation of low Earth orbit (LEO) satellites.
This innovative approach not only enhances internet access in remote and underserved areas but also demonstrates the commercial viability of satellite networks. As the demand for connectivity continues to rise, Starlink exemplifies how private companies are leading the charge in space commercialisation, paving the way for new business models and opportunities in satellite communications, data services, and beyond.
The potential for groundbreaking advancements in lunar and Mars exploration is becoming increasingly real. Private companies like SpaceX and Boeing are at the forefront of this evolution, leveraging their substantial investments and innovative capabilities to push the boundaries of what is possible in space travel. The success of Starlink has inspired numerous other ventures, contributing to a rapidly evolving landscape where private enterprises play a crucial role in shaping the future of space exploration and technology.
It appears that when humanity decides to establish internet access on the Moon, we may possess the satellite technology necessary to achieve that objective. NASA’s Artemis program and other international lunar exploration missions are considering communication technologies that could support Internet services on the Moon. For example, NASA’s Lunar Gateway project aims to create a space station in lunar orbit that could facilitate communication.
The ongoing development of reusable rocket technology is a game-changer, significantly reducing costs and enhancing the feasibility of ambitious missions to the Moon and Mars. Public-private partnerships are expected to be crucial in fostering innovation, with NASA’s initiatives inspiring collaboration with private enterprises.
These companies represent a diverse range of innovations within the space technology sector, attracting significant investments to fuel their growth and development. As the space industry continues to evolve, these companies are poised to play crucial roles in shaping the future of space exploration and commercialisation.
Conclusion
The future of space technology is full of potential, not just for exploration but also for significant financial returns. The commercial space industry is projected to grow by an impressive 41% over the next five years, driven by innovations in reusable rockets and satellite technology that are making space more accessible and cost-effective. As the space economy is projected to soar to an impressive USD 1.8 trillion by 2035, a wealth of investment opportunities will arise across various sectors, including satellite and rocket manufacturing, launch services, space mining, satellite communications, and the rapidly growing space tourism industry.
Staying updated on the latest developments in this rapidly evolving sector is crucial for investors eager to seize these opportunities. DCSC.ai offers a sophisticated, AI-driven platform that empowers investors to navigate the complexities of the space market. By providing insights into emerging technologies and identifying high-potential investment opportunities, DCSC.ai enables stakeholders to make informed decisions that align with the dynamic landscape of space innovation. The future of space tech is not just about exploration; it’s about tapping into a new economic landscape that promises significant returns for those ready to engage.

Leave a Reply