As we witness the ongoing evolution of the AI industry, it’s important to recognise the crucial role that semiconductors play in driving this progress. The development of advanced semiconductors has been instrumental in enabling the creation of powerful AI systems, a contribution that continues to shape our world today. Through the lens of the DCSC company classification system, we can identify key players in the semiconductor sector who are at the forefront of AI innovation.
For investors, grasping the connection between semiconductors and AI is vital as it opens up a realm of opportunities in the stock market. With the increasing demand for AI-driven technologies, companies specialising in AI chip development like NVIDIA, AMD, and Intel are poised to see substantial growth, making them appealing investment prospects. By keeping abreast of the latest developments in semiconductor technology, investors can tap into the promising prospects of the AI semiconductor market, which is projected to experience significant growth in the years ahead.
In fact, industry forecasts predict a revenue surge to $71 billion in 2024, marking a substantial 33% increase from the previous year. Gartner forecasts AI PC shipments will reach 22% of the total PC shipments in 2024, and by the end of 2026, 100% of enterprise PC purchases will be an AI PC. AI PCs include a neural processing unit (NPU) enabling AI PCs to run longer, quieter and cooler and have AI tasks running continually in the background, creating new opportunities for leveraging AI in everyday activities.
The year 2024 has brought a wave of transformative developments at the intersection of semiconductors and AI. The past six months have been marked by a series of exciting innovations, from the introduction of Nvidia’s cutting-edge Blackwell GPU architecture to the widespread adoption of chiplet technology, a cost-effective solution that aims to make technology more accessible in areas like healthcare, education, and communication. Not to mention the significant strides made in thermal batteries and high-bandwidth memory.
These advancements have laid the foundation for a market that is expected to achieve new record levels, with computer electronics driving nearly half of the total revenue from AI semiconductors.
According to Gartner’s latest report from Q1 2024, the industry’s ongoing innovation in chip design and manufacturing capabilities is expected to propel the market to a staggering $159 billion by 2028.
With such rapid growth on the horizon, it’s no wonder that investors are taking notice, and the AI semiconductor market is becoming an increasingly attractive destination for those looking to capitalise on the immense potential of AI-powered technologies.
In this article, we review prominent market players, examining their current presence and future potentials.
Giants in the House: Major AI Chipmakers
1. Nvidia
Nvidia has been a prominent figure in the gaming and crypto industry for years, crafting top-of-the-line graphics processing units (GPUs) that have left an indelible mark. Notably, the graphics arrays in both the Xbox and PlayStation 3 are powered by Nvidia technology.
Beyond gaming, Nvidia has ventured into the realm of AI chips, introducing groundbreaking solutions such as Xavier and Volta. Over the past year, Nvidia has emerged as a key player in the overall semiconductor industry, particularly in the field of artificial intelligence. The company’s chips are essential for the development and functioning of new AI systems.
Nvidia’s market value has increased by over 160% to $3.1 trillion since the beginning of the year, after a stellar year in 2023 too, briefly making it the world’s most valuable company in June. Nvidia’s AI chipsets are meticulously crafted to tackle a wide array of business challenges across diverse industries.
Volta, for instance, is finely tuned for data centre applications, while Xavier serves as the linchpin for autonomous driving solutions. In the domain of cloud GPUs, Nvidia has established a near-monopoly, with most cloud providers exclusively offering Nvidia GPUs for cloud computing needs. Furthermore, Nvidia’s launch of the DGX Cloud service has provided enterprises with direct access to cloud GPU infrastructure, streamlining operations and driving efficiency.
Nvidia’s recent breakthroughs, epitomised by the revolutionary Blackwell GPU architecture, have set a new standard for AI chip development, ushering in an era of swifter and more efficient processing for sophisticated AI workloads.
As the AI sector continues to evolve, Nvidia’s unwavering commitment to innovation is expected to reshape the industry landscape. It will make a profound impact on the stock market, positioning the company as an appealing prospect for those looking to invest in the future of AI.
This presents an enticing opportunity for investors to capitalise on the limitless potential of AI-driven technologies, with Nvidia’s stock performance poised to serve as a pivotal indicator of the market’s growth trajectory.
2. Microsoft
Microsoft Corporation is playing a prominent role in both the semiconductor and AI sectors, with its recent strides in AI innovation poised to transform the industry. By 2024, the company’s emphasis on developing AI-driven technologies has resulted in the introduction of state-of-the-art products, including AI chipsets that enhance the speed and efficiency of handling intricate AI workloads.
Microsoft has now claimed the title of the world’s most valuable company, boasting a market capitalisation exceeding $3.3 trillion in 2024. This remarkable ascent in the AI domain can be credited to Microsoft’s early and substantial investment in OpenAI, a key player in developing top-performing language models. Microsoft’s foray into AI has seen the integration of ChatGPT’s models into its software suite, including the innovative Copilot feature. Additionally, the company has forged partnerships with prominent AI firms like Inflection and Mistral, demonstrating its commitment to leveraging cutting-edge AI technologies.
Rather than relying solely on acquisitions, Microsoft is strategically collaborating with emerging startups to navigate regulatory challenges and foster innovation. While its primary focus remains on enterprise AI solutions, Microsoft is now setting its sights on the consumer market, aiming to drive growth through AI-enhanced products such as Copilot and Bing.
With a solid presence in cloud computing through its Azure platform, significant investments in hardware AI infrastructure, and a suite of productivity-oriented applications, Microsoft appears to have strategically positioned itself along the AI Stack for future success.
This narrative underscores the importance of considering non-traditional sectors when analysing corporate strategies in the AI landscape or elsewhere. By assessing where companies are investing and the rationale behind their decisions, one can anticipate their future endeavours and identify potential synergies within the industry. With DCSC, companies have multiple sectors attached to them at some percentage rate, which can help investors understand in which industries those companies are active.
3. Apple
Apple Inc is also making significant progress in the semiconductor and AI sectors, with its recent advancements in AI innovation poised to make a significant impact on the industry. By 2024, the company’s focus on developing AI-powered technologies has resulted in the creation of cutting-edge products, including AI chipsets that enable faster and more efficient processing of complex AI workloads.
Apple has always placed a strong emphasis on maintaining control over every aspect of its technology, from hardware to software, to ensure a seamless and consistent user experience across all its devices.
This commitment to the unique ‘Apple style design’ is evident in the company’s approach to AI and chip development, where it designs its own processors like the A series for iPhones and the M series for Macs. These chips are equipped with advanced AI capabilities, such as facial recognition and augmented reality, to enhance device performance while prioritising user privacy and security. By overseeing the chip design process, Apple ensures a close integration between hardware and software, resulting in optimised performance for AI applications. This not only sets Apple’s products apart in the market but also reduces its reliance on external chip suppliers, minimising potential disruptions in the supply chain.
Recently, Apple introduced its ‘Apple Intelligence’ initiative, featuring a proprietary on-device foundational model that, while smaller in scale compared to OpenAI’s ChatGPT, promises efficient and rapid generative AI capabilities across its extensive hardware lineup.
Emphasising local inference and edge computing, Apple distinguishes itself as a champion of privacy and security in the AI landscape, positioning itself as a developer of ‘ethical generative AI’ in contrast to its competitors.
Despite entering the AI arena relatively late, Apple remains a compelling player due to its robust integration at the higher layers of the technological stack. Looking forward, Apple Inc’s commitment to driving innovation is expected to have a substantial effect on the AI semiconductor market.
Key prospects and projects for 2024 include the integration of AI-powered technologies into its product lineup. This presents a compelling opportunity for investors to capitalise on the vast potential of AI-powered technologies, with Apple Inc’s role in the AI semiconductor market likely to drive overall market growth.
4. Alphabet (Google)
Alphabet, the parent company of Google, utilises its dominance in data and AI algorithms to reinforce its standing within the AI Stack. Google’s creation of the Tensor Processing Unit (TPU) underscores its dedication to excelling in AI hardware.
These custom-designed TPUs are engineered to accelerate machine learning tasks, significantly boosting the performance of Google’s AI services like search, voice recognition, and translation.
Additionally, Google Cloud provides access to TPUs, enabling developers and businesses to harness Google’s AI infrastructure for their own applications. By developing proprietary AI chips, Google not only enhances the efficiency of its services but also positions itself as a significant player in the cloud computing and AI sectors, directly competing with other tech giants and specialised AI chip companies.
Like Meta, Google possesses a vast reservoir of proprietary data from its consumer-centric ventures. However, its Gemini models (Gemini is a family of AI models, like OpenAI’s GPT) still lag behind those of OpenAI and have recently faced setbacks with both its chatbot and image generation tools.
Consequently, it remains uncertain if Google can streamline its AI efforts before facing stiff competition. As the demand for high-performance AI chips continues to grow, Alphabet Inc’s innovations present new opportunities and risks for its stock, making it an attractive destination for investors looking to capitalise on the vast potential of AI-powered technologies.
5. Amazon (AWS)
Amazon Inc is also making significant strides in the semiconductor and AI industries, with its latest advancements in AI innovation poised to have a profound impact on the market. Amazon has ventured into designing its own chips for generative AI applications on cloud computing services, although the actual manufacturing is outsourced to third-party semiconductor foundries, notably TSMC. This strategic shift aligns with a broader industry trend where tech giants are increasingly bringing chip design in-house to enable customization that better suits specific cloud-based AI tasks than off-the-shelf components.
Amazon’s development of the Graviton and Inferentia chips tailored for its AWS cloud computing environment exemplifies this approach, optimising operational efficiencies. AWS Inferentia accelerators are designed by AWS to deliver high performance at the lowest cost in Amazon EC2 for deep learning (DL) and generative AI inference applications.
By leveraging its proprietary chips, Amazon can seamlessly integrate hardware and software, leading to enhanced performance for AI services such as voice recognition, language translation, and data analytics. This move not only enhances the capabilities of AWS but also grants Amazon greater control over its supply chain, reducing reliance on external chip suppliers.
Starting from its core platform function, Amazon pursues vertical integration to customise its hardware to the precise requirements of its cloud services, enhancing performance and reducing costs in its cloud business. By designing its own chips like the Amazon Graviton processors, the company can decrease its dependence on third-party suppliers, mitigating risks associated with supply chain disruptions and fluctuations in supplier pricing.
This strategic approach not only bolsters Amazon’s competitive advantage by improving the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of its services but also affords greater control over the technological trajectory of its infrastructure, enabling swift adaptation to the evolving demands of AI applications.
However, while Amazon has established partnerships with AI companies like Anthropic, these collaborations are not exclusive, and its ownership of predominantly retail-related data limits its unique resources to dominate the AI Stack.
Additionally, Amazon Q, a generative AI-powered assistant designed for work, is a testament to the company’s commitment to driving innovation forward. With key prospects and projects for 2024 including the development of Amazon FemTech (Femtech is a term that refers to diagnostic tools, products, services, wearables and software that use technology to address women’s health issues), Amazon Inc’s role in the AI semiconductor market is likely to be a key factor in the market’s overall growth.
For investors, this presents a compelling opportunity to capitalise on the vast potential of AI-powered technologies, with Amazon’s current market value approximately standing at $2.06 trillion and its AI-powered product development and services expected to drive revenue growth and industry growth in 2024 and beyond.
6. META
Meta Platforms Inc is also actively involved in the semiconductor and AI sectors, with its subsidiary Meta AI leading the charge in driving innovation. The company is set to unveil the next generation of its custom-designed chips tailored for AI workloads, exploring the integration of generative AI technology in metaverse games, and releasing new AI research models to accelerate large-scale innovation.
Meta’s new strategy involves the adoption of an open-source approach as a platform company, aligning with its goal to develop leading AI models and overcome existing bottlenecks. Zuckerberg recently highlighted Meta’s advantage in the ‘AI race’ due to its solid access to valuable Nvidia H100 graphics cards for training AI models. Additionally, Meta’s wealth of training data from its social media platforms, including Instagram, Facebook, and WhatsApp, positions it as a leader in natural-sounding conversations with its latest LLaMa LLM model.
Similar to Amazon, Meta plans to introduce custom-designed chips for its data centres in 2024, although manufacturing will be outsourced to other companies. With a strong focus on AI-powered technologies, Meta Platforms Inc is poised to make a significant impact on the AI semiconductor market.
This presents an appealing opportunity for investors to tap into the immense potential of AI-
powered technologies, especially considering Meta Platforms Inc’s stock valuation reflecting expected earnings growth of 14.50% next year and 14% in 2025.
7. Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company (TSMC)
A key player in the semiconductor and AI industries, TSMC is at the forefront of driving innovation. As the world’s largest semiconductor foundry with a commanding 61.7% market share in the global semiconductor foundry market, TSMC is pioneering advancements in leading-edge technology, including AI chip development, high-bandwidth memory, and chiplet technology.
With pivotal projects and prospects for 2024 focusing on new chip designs, manufacturing capabilities, and AI-powered technologies, TSMC is well-positioned to fuel revenue growth and expand its market share in the AI semiconductor market. As the global semiconductor market is anticipated to grow by 13.1% in 2024, and with TSMC projecting a potential 30% increase in second-quarter sales due to the rising demand for semiconductors supporting artificial intelligence applications, investors are taking note of TSMC’s contributions to AI and semiconductors, offering promising investment opportunities.
8. Broadcom
Broadcom, a prominent player in the semiconductor and AI industries, is poised to take significant strides in 2024. With AI sales forecasted to surpass $11 billion in fiscal 2024, the company is collaborating with China’s ByteDance on the development of an advanced AI processor and is actively working on AI-powered technologies, including a generative AI-driven knowledge assistant.
Key initiatives and projects for 2024 involve the development of advanced AI chips in partnership with ByteDance, expansion of AI-powered technologies, and a focus on enhancing AI chip development and manufacturing capabilities.
Broadcom’s innovations are expected to drive revenue growth and bolster market share in the AI semiconductor market. With a significant rise in its stock value over the past year, outperforming industry peers, Broadcom’s strides in AI and semiconductors present enticing investment opportunities, albeit accompanied by associated risks.
As the company’s growth in AI sales and market share could lead to increased revenue and stock price growth, investors are closely monitoring Broadcom’s role in propelling innovation in the AI semiconductor market.
9. New Players on the Horizon: Leading AI Chip Startups
According to a recent 06/2024 Bloomberg report, a team founded by college dropouts has raised $120 million from investors led by Primary Venture Partners to build a new AI chip to take on Nvidia.
Etched is a new startup focused on developing a specialised AI chip, the Sohu AI chip, tailored for transformer models like OpenAI’s ChatGPT. By targeting this specific application, Etched aims to offer faster and more cost-effective solutions for powering large language models, which are increasingly important in various AI applications.
Collaborating with TSMC’s Emerging Businesses Group is a significant partnership that can provide access to advanced semiconductor manufacturing technologies and expertise. Etched’s approach to developing a specialised AI chip for transformer models shows a keen understanding of the market needs and aligns with the growing demand for efficient and powerful AI solutions.
This strategic direction, combined with strong partnerships and a talented team, positions Etched well for success in the competitive AI semiconductor market.
Several other independent startups have recognised and are keen to capitalise on the growth in demand for chips due to the rise of artificial intelligence. SambaNova Systems was established in 2017 with the objective of creating advanced hardware-software systems for high-volume generative AI tasks. The company has created the SN40L chip and secured over $1.1 billion in funding.
Another rising star could be Groq. Founded by ex-Google employees, the startup introduces LPUs, a fresh approach to AI chip architecture designed to streamline system adoption for businesses. Headquartered in Silicon Valley, Groq provides cloud and on-prem solutions at scale for AI applications.
In 2022, Groq completed the acquisition of Maxeler, a company renowned for its specialised high-performance computing solutions designed specifically for the financial services industry. With an initial funding of approximately $350 million, the company has rolled out products like the GroqChip™ Processor and GroqCard™ Accelerator. By Q1 2024, the company reported 70,000 developers signed up on their cloud platform.
Graphcore is also a strong contender with promising potential. It is a British startup founded in 2016. The company announced its flagship AI chip as IPU-POD256. Graphcore has already been funded with around $700 million. The company has established strategic collaborations with leading data storage companies such as DDN, Pure Storage, and Vast Data. Graphcore also collaborates with prestigious research institutions worldwide, including the Oxford-Man Institute of Quantitative Finance, the University of Bristol, and the University of California, Berkeley.
In summary, the importance of key players such as NVIDIA, AMD, Intel, and other industry leaders in the semiconductor and AI sectors is paramount. Looking towards 2025, there are substantial opportunities for growth and advancement in these industries, particularly with the anticipated significant expansion of the AI semiconductor market.
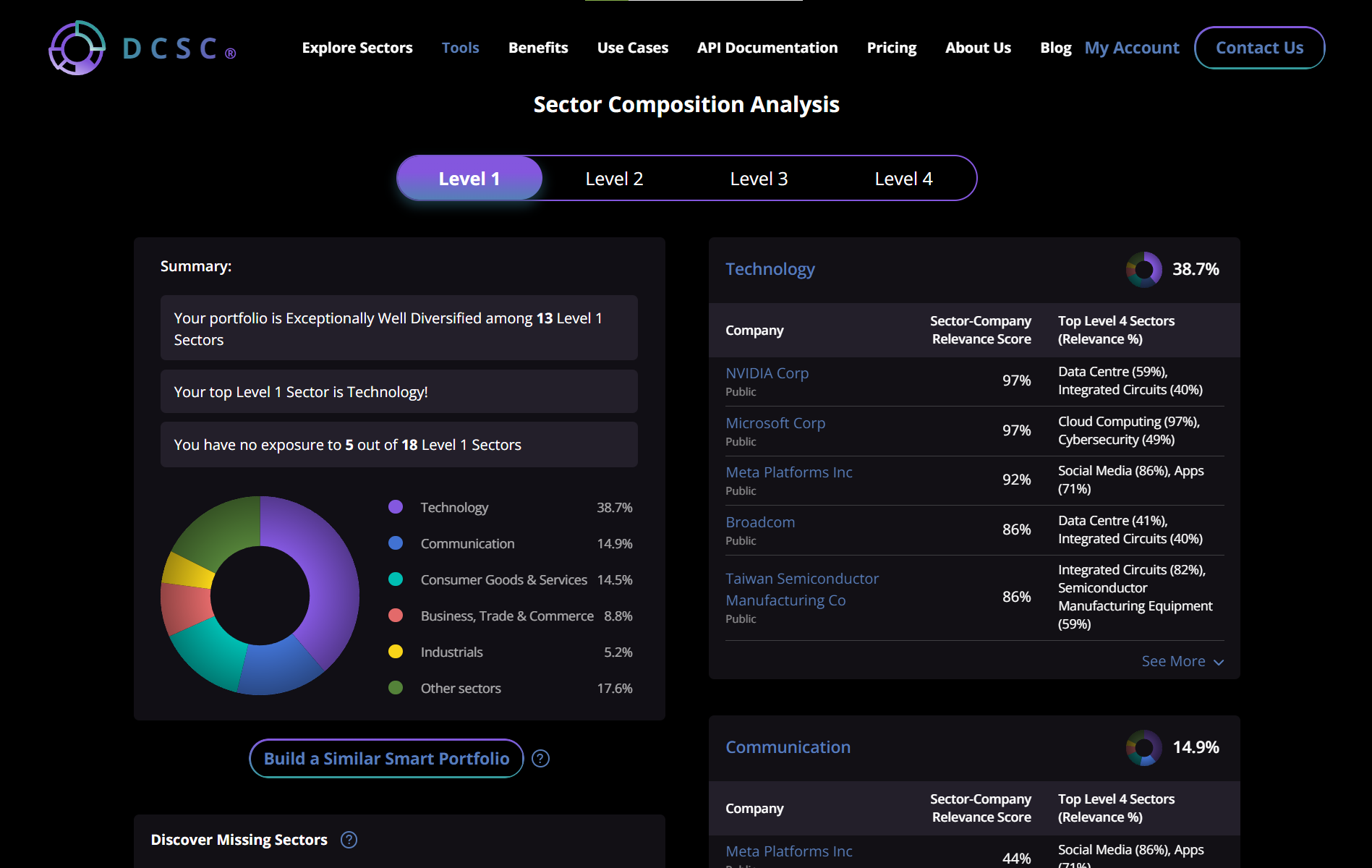
The DCSC company classification system breaks these companies down into their traditional sectors, their AI/semiconductor components, and the other industries in which they have a stake.
DCSC’s Analysis of These Companies
Traditional classification systems put Amazon, Google, etc. into a single sector at various levels. But that does not reflect the reality of how these companies operate, especially when it comes to intersectoral activities like semiconductors (is that tech, consumer goods, industrials?). DCSC offers a new perspective on sector classification over 4 levels and with dynamic scoring.
For instance, Alphabet (Google) has the highest Level 4 relevance scores at 74% for smartphones and 51% for search engines. Interestingly, Google’s exposure to the smartphone market is now greater than that of its search engine business. The company operates in several Level 1 sectors, including technology (45.9%), Consumer Goods & Services (17.1%), Communication (14.9%), Consulting & Professional Services (11.7%), and Business, Trade & Commerce (10.1%).
Another example is Broadcom. According to DCSC, the company operates in Technology (44.3%), Communication (21.6%), Energy (15.9%), Consumer Goods & Services (10.8%), and Industrials (7.2%). The relevance scores for its top four sector classifications indicate that Broadcom’s Data Center relevance (41%) is nearly on par with its integrated circuits manufacturing relevance (40%).
A final example, Graphcore is a recent chip manufacturer startup based in the UK. The relevance scores for its top sectors indicate that the company primarily focuses on computer hardware (28%) and is significantly investing in neural networks (24%), effectively integrating these two areas into its products and solutions.
DCSC and its tools can be used to invest thematically – e.g., for robotics and semiconductors – or to analyse an existing portfolio for its sector exposures. These can highlight interesting facts and the exposure of individual companies to different sectors, improving your due diligence and monitoring of related sectors, even those that may traditionally be unexpected.










Leave a Reply